Home » Knee Replacement Surgery
GET OFFER
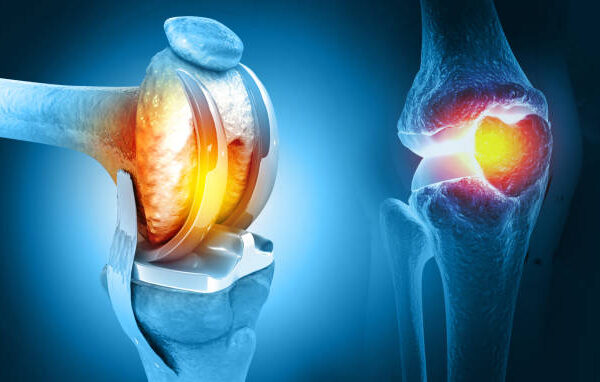
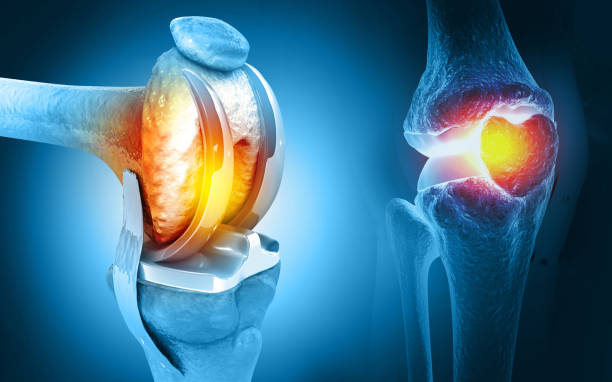
Knee replacement surgery, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure to replace damaged or worn-out parts of the knee joint with artificial components called implants or prostheses. It is commonly performed to relieve pain, restore mobility, and improve quality of life for individuals suffering from severe knee conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or trauma-induced damage.
Indications for Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee replacement surgery is recommended for individuals who:
- Experience severe knee pain that limits daily activities like walking, climbing stairs, or standing.
- Suffer from knee stiffness that impairs mobility.
- Have not found relief through non-surgical treatments such as medications, physical therapy, or injections.
- Present with conditions like:
- Osteoarthritis: The most common cause of joint damage.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune condition leading to joint inflammation.
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis: Joint damage following an injury.
- Deformities: Bow-legged or knock-knee conditions causing uneven stress on the joint.
Types of Knee Replacement Surgery
- Total Knee Replacement (TKR):
- Entire knee joint is replaced, including the femur, tibia, and patella surfaces.
- Partial Knee Replacement (PKR):
- Only the damaged portion of the knee is replaced, preserving healthy bone and tissue.
- Revision Knee Replacement:
- A second surgery to replace or repair a previously implanted prosthesis.
- Minimally Invasive Knee Replacement:
- Uses smaller incisions and specialized instruments for reduced recovery time.
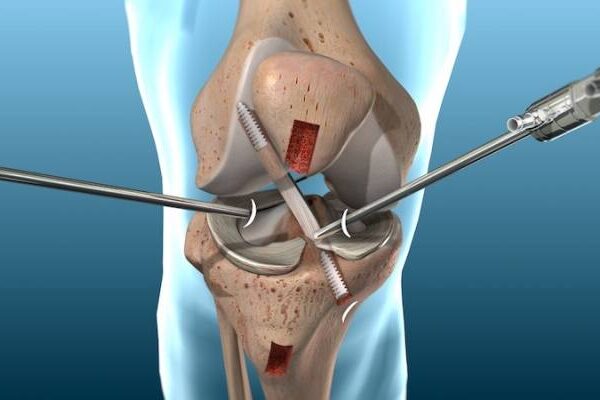
The Procedure
- Preoperative Preparations:
- Comprehensive evaluation, including X-rays, MRI, or CT scans, to plan the surgery.
- Stopping certain medications and fasting prior to the procedure.
- During Surgery:
- Performed under regional or general anesthesia.
- An incision is made over the knee to access the joint.
- Damaged bone and cartilage are removed and replaced with artificial components made of metal, ceramic, or plastic.
- The prosthesis is secured with cement or press-fit techniques.
- Closure:
- The incision is closed with sutures or staples, and a sterile dressing is applied.
- Postoperative Care:
- Patients are monitored in a recovery room before being transferred to a hospital room or discharged home.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
- Immediate Postoperative Care:
- Pain is managed with medications, and anticoagulants are administered to prevent blood clots.
- Physical therapy begins within 24 hours to encourage mobility and prevent stiffness.
- Physical Therapy:
- Gradual strengthening and range-of-motion exercises tailored to individual progress.
- Use of assistive devices like walkers or crutches initially.
- Long-Term Recovery:
- Most patients regain mobility within 6–8 weeks.
- Full recovery, including resuming high-impact activities, may take 3–6 months.
Benefits of Knee Replacement Surgery
- Pain Relief: Significant reduction or elimination of chronic knee pain.
- Improved Mobility: Restores the ability to perform daily activities.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Allows for greater independence and activity participation.
- Durability: Modern implants often last 15–20 years or more.
Risks and Complications
While knee replacement surgery is highly successful, potential risks include:
- Infection at the surgical site.
- Blood clots in the legs or lungs (deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism).
- Stiffness or reduced range of motion.
- Prosthetic wear or loosening over time.
- Rarely, nerve or blood vessel injury.
Innovative Techniques in Knee Replacement Surgery
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery:
- Enhances precision in implant positioning and alignment.
- Custom Knee Implants:
- Personalized prostheses designed using 3D imaging for better fit and functionality.
- Minimally Invasive Techniques:
- Smaller incisions and less tissue disruption for quicker recovery.
- Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) Protocols:
- Optimized pain management and rehabilitation for reduced hospital stays.
20 Questions & Answers on Knee Replacement Surgery
1. What is knee replacement surgery?
It is a procedure to replace damaged knee joint surfaces with artificial implants to relieve pain and improve mobility.
2. Who needs knee replacement surgery?
Patients with severe knee pain, stiffness, or joint damage that does not respond to non-surgical treatments.
3. What are the types of knee replacement surgery?
Total knee replacement, partial knee replacement, revision surgery, and minimally invasive knee replacement.
4. How long does the surgery take?
The procedure typically lasts 1–2 hours.
5. What materials are used for knee implants?
Common materials include metal alloys, ceramics, and high-density polyethylene.
6. How long do knee implants last?
Modern implants can last 15–20 years or more with proper care.
7. Is knee replacement painful?
Postoperative pain is expected but is effectively managed with medications and therapy.
8. How soon can I walk after surgery?
Most patients begin walking with assistance within 24–48 hours.
9. How long is the hospital stay?
Hospital stays typically last 1–3 days, depending on the procedure and individual recovery.
10. When can I return to work after knee replacement surgery?
Desk jobs may resume in 2–4 weeks, while physically demanding jobs may require 3–6 months.
11. Will I need physical therapy?
Yes, physical therapy is crucial for restoring strength, mobility, and function.
12. Can I kneel or squat after knee replacement?
It may feel uncomfortable, but many patients can kneel or squat with practice and guidance.
13. Are there risks associated with knee replacement surgery?
Yes, risks include infection, blood clots, stiffness, and prosthetic loosening.
14. What is robotic-assisted knee replacement?
It uses advanced technology for precise implant placement, improving outcomes and longevity.
15. Can younger patients undergo knee replacement?
Yes, especially with advancements in implant materials, it is suitable for younger, active individuals.
16. Can knee replacement surgery treat arthritis?
Yes, it is highly effective for severe arthritis that affects joint surfaces.
17. How can I prepare for knee replacement surgery?
Follow preoperative instructions, such as fasting, stopping certain medications, and preparing your home for recovery.
18. What happens if I delay knee replacement surgery?
Delaying surgery can lead to worsening pain, reduced mobility, and potential complications in surrounding joints.
19. Is knee replacement covered by insurance?
Yes, it is generally covered if deemed medically necessary.
20. What lifestyle changes are recommended after knee replacement?
Maintain a healthy weight, stay active with low-impact exercises, and avoid high-impact activities to prolong implant life.