Home » HIP Replacement Surgery
GET OFFER
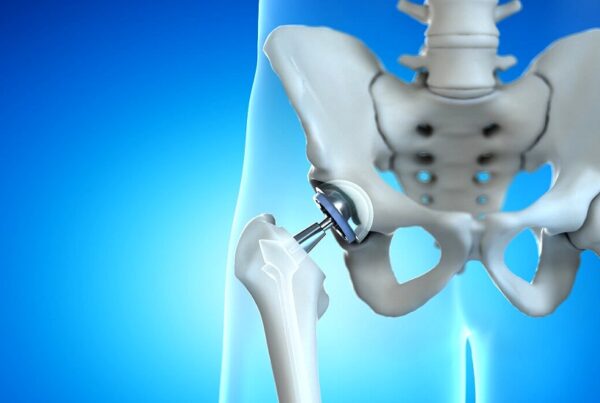
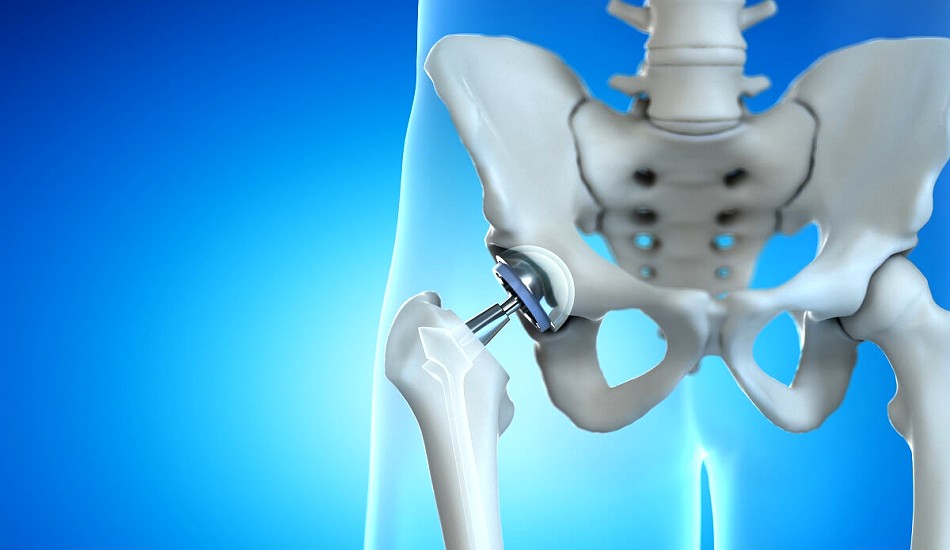
Hip replacement surgery, also known as hip arthroplasty, is a common procedure to replace a damaged or diseased hip joint with an artificial implant. It is typically performed to relieve pain, restore mobility, and improve quality of life for individuals with severe hip conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or fractures. Below is a comprehensive explanation of the procedure, recovery, and treatment options, followed by a Q&A section.
Indications for Hip Replacement Surgery
Hip replacement is generally recommended for individuals who:
- Experience severe pain that interferes with daily activities, such as walking or climbing stairs.
- Have significant joint stiffness that limits movement.
- Do not respond to non-surgical treatments like medications, physical therapy, or lifestyle changes.
- Suffer from conditions such as:
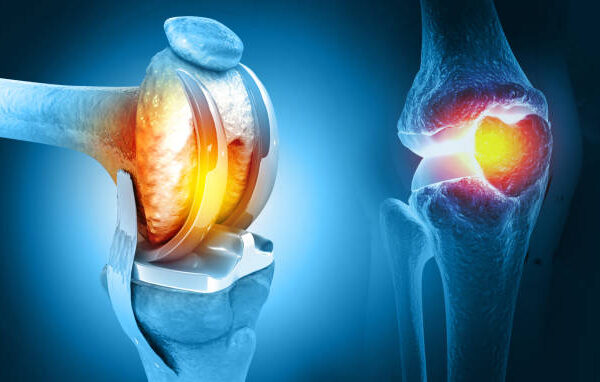
- Osteoarthritis: The most common cause, leading to cartilage wear and tear.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An inflammatory condition causing joint damage.
- Hip Fractures: Trauma that disrupts the joint.
- Avascular Necrosis: Death of bone tissue due to limited blood supply.
Types of Hip Replacement Surgery
- Total Hip Replacement (THR):
- Both the ball (femoral head) and socket (acetabulum) of the hip joint are replaced with prosthetic components.
- Partial Hip Replacement (Hemiarthroplasty):
- Only the femoral head is replaced, usually performed after specific types of fractures.
- Hip Resurfacing:
- The damaged surface of the femoral head is capped with a smooth metal covering instead of being fully replaced. This is more common in younger, active patients.
Surgical Procedure
- Preparation:
- Preoperative evaluations, including blood tests, imaging (X-rays or MRI), and physical examinations, are conducted.
- Patients are instructed to stop certain medications and prepare their home for recovery.
- During Surgery:
- Performed under general or regional anesthesia.
- An incision is made to access the hip joint.
- The damaged bone and cartilage are removed and replaced with artificial components made of metal, ceramic, or plastic.
- Postoperative Care:
- Patients typically spend 1–3 days in the hospital.
- Pain management, early mobilization, and physical therapy are prioritized to ensure proper healing.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
- Immediate Recovery:
- Patients begin walking with assistance (walker or crutches) within 24–48 hours after surgery.
- Pain and swelling are managed with medications and ice therapy.
- Physical Therapy:
- A tailored exercise program helps restore strength, flexibility, and mobility.
- Emphasis on avoiding high-impact activities during the early recovery phase.
- Long-Term Recovery:
- Full recovery can take 3–6 months, depending on individual health and adherence to rehabilitation.
Risks and Complications
While hip replacement surgery has a high success rate, potential risks include:
- Infection at the surgical site.
- Blood clots in the legs or lungs (deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism).
- Dislocation of the artificial joint.
- Wear and tear of the prosthetic components over time, necessitating revision surgery.
- Nerve or blood vessel injury.
Innovative Techniques
- Minimally Invasive Surgery:
- Smaller incisions and reduced muscle disruption lead to faster recovery and less pain.
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery:
- Enhances precision during implant placement, reducing complications and improving outcomes.
- Advanced Prosthetic Materials:
- Use of durable materials such as highly cross-linked polyethylene, ceramic-on-ceramic, or metal-on-metal combinations for longevity.
20 Questions & Answers on Hip Replacement Surgery
1. What is hip replacement surgery?
It is a procedure to replace a damaged hip joint with artificial components to relieve pain and restore mobility.
2. Who needs hip replacement surgery?
Patients with severe hip pain, stiffness, or joint damage due to arthritis, fractures, or other conditions.
3. What are the main types of hip replacement surgery?
Total hip replacement, partial hip replacement, and hip resurfacing.
4. How long does hip replacement surgery take?
The procedure typically takes 1–2 hours.
5. What materials are used for hip implants?
Metal alloys, ceramics, and high-density polyethylene are common materials.
6. How long do hip implants last?
Modern implants often last 15–20 years or longer.
7. Is hip replacement painful?
Pain is expected initially, but effective pain management strategies ensure a manageable recovery.
8. How soon can I walk after surgery?
Most patients start walking with assistance within 24–48 hours.
9. What are the risks of hip replacement surgery?
Infection, blood clots, joint dislocation, and implant wear are potential risks.
10. How can I prepare for hip replacement surgery?
Undergo preoperative evaluations, stop certain medications, and prepare your home for a safe recovery.
11. Can hip replacement surgery be done minimally invasively?
Yes, minimally invasive techniques reduce recovery time and surgical trauma.
12. How long does recovery take?
Full recovery takes 3–6 months, depending on individual progress and therapy adherence.
13. What is the success rate of hip replacement surgery?
The procedure has a high success rate, with over 90% of patients experiencing significant pain relief and improved mobility.
14. Can hip replacement surgery be repeated?
Yes, revision surgery can replace worn or damaged implants.
15. Will I need physical therapy after surgery?
Yes, physical therapy is crucial for regaining strength and mobility.
16. Are there activities to avoid after surgery?
High-impact activities like running and jumping should be avoided to protect the implant.
17. Can younger people have hip replacement surgery?
Yes, advancements in prosthetics make it a viable option for younger, active patients.
18. How can I prevent complications after surgery?
Follow your surgeon’s advice, attend physical therapy, and avoid risky movements or activities.
19. Is hip replacement surgery covered by insurance?
Most health insurance plans cover the procedure, but coverage details vary.
20. What happens if I delay hip replacement surgery?
Delaying can lead to worsening pain, decreased mobility, and potential complications in other joints or the spine due to compensatory movements.